ASTM A672 Standard and Steel Pipe Grade Overview

Faced with the challenge of selecting a pipeline for complex working conditions, including oil and gas transmission projects, the ASTM A672 pipe provides engineers with reliable material solutions through scientific grade classification. This article will systematically analyze how to find the right steel grades with engineering requirements.
ASTM A672 Standard Definition
ASTM A672 is a standard for electric fusion (arc) welded pressure pipes developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials, suitable for medium and high pressure (usually ≥5MPa) and low temperature (-29°C to +343°C extension) environments. It is a similar standard of API 5L, Its core application areas include:
Oil and gas transportation, Power plant steam system, Chemical process piping, Pressure infrastructure requiring high reliability.




Manufacturing and Quality Control of ASTM A672 Pipe

As the core standard for high-pressure electric fusion-welded pipes, ASTM A672 ensures the integrity of the pipe in harsh environments through dual control of the base material's strength grade (Grade) and manufacturing level (Class). Understanding this table is the basis for selection.
(Note: The following focuses on the most commonly used B60, C65, and B70 grades)
| Key links | Technical requirements |
|---|---|
| Substrate | Pressure vessel grade plates (such as ASTM A516) |
| Molding process | Electrofusion welding (EFW) |
| Post-processing | Forced heat treatment + non-destructive testing (UT/RT) |
| Grade/Level Definition |
Grade: Material strength (e.g. B60) Class: Manufacturing standard (e.g. Class 22 = normalizing + tempering + 100% UT) |
Mechanical Performance Comparison and Application
The 3 most commonly used grades, B60, C65 and B70, form a continuous performance ladder. The following table compares key parameters to help you quickly locate the optimal solution that meets pressure, temperature and cost constraints.
| Parameter | ASTM A672 B60 | ASTM A672 C65 | ASTM A672 B70 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate Standard | A516 Gr.60 | A516 Gr.65 | A516 Gr.70 |
| Yield Strength | ≥220 MPa | ≥240 MPa | ≥260 MPa |
| tensile strength | 380-515 MPa | 415-550 MPa | 485-620 MPa |
| Applicable pressure range | <3.5 MPa | 3.5-7 MPa | >7 MPa |
| Applicable temperature limit | ≤350°C | ≤400°C | ≤480°C (short term) |
| Weldability | Excellent | excellent | Heat input needs to be controlled |
| Cost Positioning | Economical | Balanced | High performance |
| Core Advantages | Easy to process, low cost | Pressure/temperature fluctuation adaptability | High pressure and high temperature bearing capacity |
ASTM A672 Typical Applications (by level)



ASTM A672 B60: Economical solution
As an entry-level option, the B60 offers excellent value for money in low-pressure/normal-temperature systems. It is the most economical choice when operating conditions are mild and budgets are limited.
-
Applicable industries:
- Stable low temperature environment (-20°C~120°C)
- Non-corrosive medium (pH 6-8)
- System pressure ≤3.5 MPa
- Cost-sensitive projects
-
Working conditions
- Municipal water supply system
- Normal pressure industrial fluid transportation (compressed air, nitrogen)
- Wastewater treatment pipeline
- Non -load-bearing structure support
The low-pressure nitrogen pipeline network (pressure 2.8MPa, temperature 40°C) of a chemical plant uses B60 pipelines and has zero failures in 10 years of operation and maintenance.
ASTM A672 C65: Industrial Main Grade
In the field of dynamic working conditions, C65 has become the first choice for medium-pressure systems due to its balanced performance parameters. Its excellent anti-fluctuation ability can effectively cope with the stress challenges brought by temperature and pressure changes.
-
Applicable industries :
- Medium-pressure steam system (secondary steam/condensate)
- Chemical heat exchanger pipeline
- Regional natural gas distribution network
- Food and pharmaceutical process pipeline
-
Working condition characteristics :
- Frequent temperature fluctuations (ΔT>100°C/day)
- Weakly corrosive media (Cl⁻<50ppm)
- System pressure 3.5-7 MPa
- Life cycle cost needs to be balanced
The refinery heat exchanger network (pressure 5.2MPa, temperature 280°C) uses C65 pipes, which have excellent thermal fatigue resistance.
-
Typical cases :
- Medium-pressure steam system (secondary steam/condensate)
- Chemical heat exchanger pipeline
- Regional natural gas distribution network
- Food and pharmaceutical process pipeline
ASTM A672 B70: First Choice for Harsh Working Conditions
For extreme working conditions such as high pressure and high temperature, B70 provides industry-leading pressure bearing capacity and durability. In critical pipelines where safety is paramount, it is a proven and reliable choice.
-
Applicable industries :
- Main steam pipeline of high-pressure boiler
- Deep well oil and gas reinjection system
- High-pressure pipeline of LNG receiving station
- Nuclear power non-nuclear thermal system
-
Working condition characteristics :
- Continuous high temperature (>350°C) or thermal shock
- High corrosion risk (H₂S/CO₂ environment)
- System pressure ≥7 MPa
- Zero fault tolerance safety requirements
Typical Cases :
The main steam pipeline of the supercritical coal-fired power plant (pressure 26MPa, temperature 565°C) adopts B70+Class 32, with a service life of over 200,000 hours.
Engineering Selection Decision Process
Scientific selection requires a systematic methodology. This process converts complex operating parameters into a three-step decision model to help you avoid common design pitfalls.
Step 1: Definition of Key Parameters
Pressure and temperature constitute the basic coordinates for selection. By dividing the parameter threshold, the candidate ASTM A672 grade range can be quickly locked.
chart:
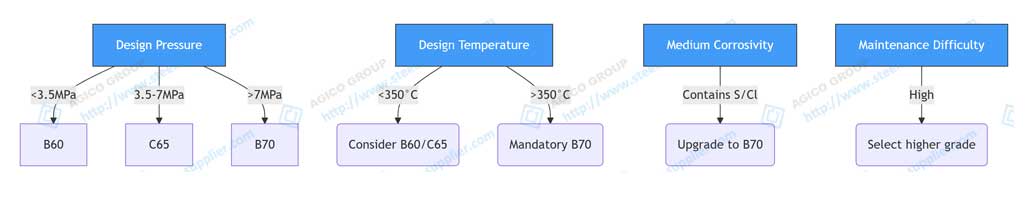
Step 2: Industry Matching Rules
Different industries have specific selection logic. This matching matrix extracts the core selection rules in the ASTM A672 application fields of power generation, chemical industry, energy, etc.
| Industry | Recommended level | Disabling Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal power generation | Main steam→B70, condensate→C65 | B60 is used for systems >5MPa |
| Petrochemical | Reactor → B70, Heat exchange → C65 | C65 is used for concentrated acid and alkaline media |
| Natural gas transmission | Main line→B70, branch line→C65 | B60 for sour natural gas |
Step 3: Avoiding Cost Traps
Wrong selection may lead to chain risks. These warning points verified by accident cases will help you to establish a reasonable balance between cost and safety.
- Over-design: Using B70 in cooling water system increases cost by 30%
- Ignoring Class Level: Failure to specify NDT level leads to weld failure
- Welding process mismatch: B70 does not use low-hydrogen welding materials, causing hydrogen embrittlement cracking
Key points in ASTM A672 Standard Application

A technical memorandum that condenses the core principles of selection. Mastering these key terms can significantly improve the accuracy and compliance of standard application.
- Uniform terminology: Strictly distinguish between " Grade " (material strength) and " Class " (manufacturing standard)
- Core logic of model selection: pressure/temperature determines the basic level → corrosiveness/maintenance requirements adjustment → budget confirmation Class level
- Failure warning: B60 is prohibited in systems with pressure fluctuations > 20%; B70 welding requires preheating above 150°C
- Extended application: Supplementary requirements for impact tests are required for low temperature conditions (-45°C)
Get Suggestions from AGICO on ASTM A672 Grade
ASTM A672 covers industrial needs from conventional facilities to extreme environments through the gradient design of B60/C65/B70. Engineers should make grade decisions based on clear design boundary conditions (ASME B31.3 pressure-temperature curve) and combined with life cycle cost analysis (LCCA). The cases and selection models mentioned in this article have been verified to be reliable in actual projects from AGICO and can be used as a quick reference tool for engineering practice.


